DP-203: Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
You build a data warehouse in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool.
Analysts write a complex SELECT query that contains multiple JOIN and CASE statements to transform data for use in inventory reports. The inventory reports will use the data and additional WHERE parameters depending on the report. The reports will be produced once daily.
You need to implement a solution to make the dataset available for the reports. The solution must minimize query times.
What should you implement?
an ordered clustered columnstore index
a materialized view
result set caching
a replicated table
Answer is a materialized view
Materialized views for dedicated SQL pools in Azure Synapse provide a low maintenance method for complex analytical queries to get fast performance without any query change.
Incorrect Answers:
C: One daily execution does not make use of result cache caching.
Note: When result set caching is enabled, dedicated SQL pool automatically caches query results in the user database for repetitive use. This allows subsequent query executions to get results directly from the persisted cache so recomputation is not needed. Result set caching improves query performance and reduces compute resource usage. In addition, queries using cached results set do not use any concurrency slots and thus do not count against existing concurrency limits.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql-data-warehouse/performance-tuning-materialized-views
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql-data-warehouse/performance-tuning-result-set-caching
You have an Azure Synapse Analytics workspace named WS1 that contains an Apache Spark pool named Pool1.
You plan to create a database named DB1 in Pool1.
You need to ensure that when tables are created in DB1, the tables are available automatically as external tables to the built-in serverless SQL pool.
Which formats should you use for the tables in DB1?
CSV
ORC
JSON
Parquet
Answer is CSV and Parquet are both correct answers.
Serverless SQL pool can automatically synchronize metadata from Apache Spark. A serverless SQL pool database will be created for each database existing in serverless Apache Spark pools.
For each Spark external table based on Parquet or CSV and located in Azure Storage, an external table is created in a serverless SQL pool database.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql/develop-storage-files-spark-tables
You are designing a financial transactions table in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool. The table will have a clustered columnstore index and will include the following columns:
● TransactionType: 40 million rows per transaction type
● CustomerSegment: 4 million per customer segment
● TransactionMonth: 65 million rows per month
AccountType: 500 million per account type

You have the following query requirements:
● Analysts will most commonly analyze transactions for a given month.
● Transactions analysis will typically summarize transactions by transaction type, customer segment, and/or account type
You need to recommend a partition strategy for the table to minimize query times.
On which column should you recommend partitioning the table?
CustomerSegment
AccountType
TransactionType
TransactionMonth
Answer is TransactionMonth
For optimal compression and performance of clustered columnstore tables, a minimum of 1 million rows per distribution and partition is needed. Before partitions are created, dedicated SQL pool already divides each table into 60 distributed databases.
Example: Any partitioning added to a table is in addition to the distributions created behind the scenes. Using this example, if the sales fact table contained 36 monthly partitions, and given that a dedicated SQL pool has 60 distributions, then the sales fact table should contain 60 million rows per month, or 2.1 billion rows when all months are populated. If a table contains fewer than the recommended minimum number of rows per partition, consider using fewer partitions in order to increase the number of rows per partition.
Reference:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/partitioning-distribution-azure-synapse-analytics-swapnil-mule
You have an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool named Pool1. Pool1 contains a partitioned fact table named dbo.Sales and a staging table named stg.Sales that has the matching table and partition definitions.
You need to overwrite the content of the first partition in dbo.Sales with the content of the same partition in stg.Sales. The solution must minimize load times.
What should you do?
Insert the data from stg.Sales into dbo.Sales.
Switch the first partition from dbo.Sales to stg.Sales.
Switch the first partition from stg.Sales to dbo.Sales.
Update dbo.Sales from stg.Sales.
Answer is Switch the first partition from stg.Sales to dbo.Sales.
Since the need is to overwrite dbo.Sales with the content of stg.Sales. SWITCH source TO target
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql/best-practices-dedicated-sql-pool
You are designing a slowly changing dimension (SCD) for supplier data in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool.
You plan to keep a record of changes to the available fields.
The supplier data contains the following columns.
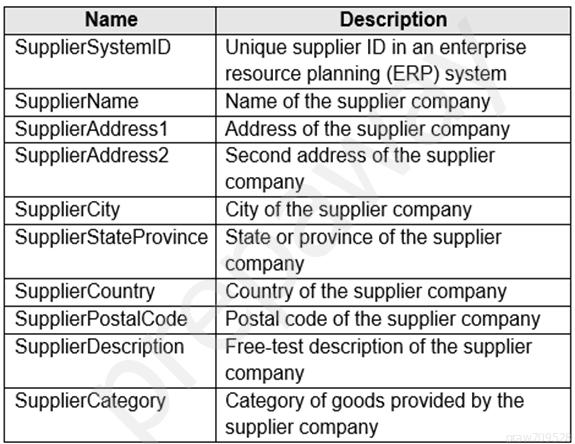
Which three additional columns should you add to the data to create a Type 2
surrogate primary key
effective start date
business key
last modified date
effective end date
foreign key
Answers are surrogate primary key, effective start date, effective end date
A type 2 SCD requires a surrogate key to uniquely identify each record when versioning. See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/populate-slowly-changing-dimensions-azure-synapse-analytics-pipelines/3-choose-between-dimension-types
under SCD Type 2 “ the dimension table must use a surrogate key to provide a unique reference to a version of the dimension member.” A business key is already part of this table - SupplierSystemID. The column is derived from the source data.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/integration-services/data-flow/transformations/slowly-changing-dimension-transformation
You have a Microsoft SQL Server database that uses a third normal form schema.
You plan to migrate the data in the database to a star schema in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool.
You need to design the dimension tables. The solution must optimize read operations.
What should you include in the solution?
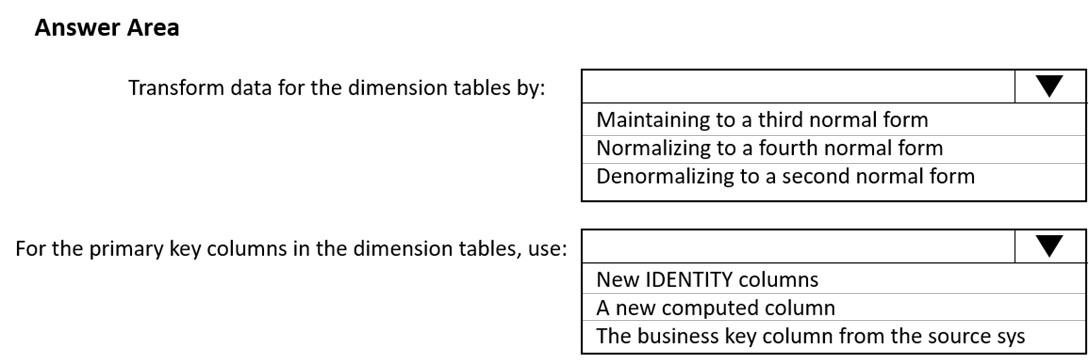
Box 1: Denormalize to a second normal form
Denormalization is the process of transforming higher normal forms to lower normal forms via storing the join of higher normal form relations as a base relation.
Denormalization increases the performance in data retrieval at cost of bringing update anomalies to a database.
Box 2: New identity columns
The collapsing relations strategy can be used in this step to collapse classification entities into component entities to obtain flat dimension tables with single-part keys that connect directly to the fact table. The single-part key is a surrogate key generated to ensure it remains unique over time.
Example:

Note: A surrogate key on a table is a column with a unique identifier for each row. The key is not generated from the table data. Data modelers like to create surrogate keys on their tables when they design data warehouse models. You can use the IDENTITY property to achieve this goal simply and effectively without affecting load performance.
Reference:
https://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertip/5614/explore-the-role-of-normal-forms-in-dimensional-modeling/
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-tables-identity
You are designing a partition strategy for a fact table in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool. The table has the following specifications:
● Contain sales data for 20,000 products.
● Use hash distribution on a column named ProductID.
● Contain 2.4 billion records for the years 2019 and 2020.
Which number of partition ranges provides optimal compression and performance for the clustered columnstore index?
40
240
400
2,400
Answer is 40
Each partition should have around 1 millions records. Dedication SQL pools already have 60 partitions.
We have the formula: Records/(Partitions*60)= 1 million
Partitions= Records/(1 million * 60)
Partitions= 2.4 x 1,000,000,000/(1,000,000 * 60) = 40
Note: Having too many partitions can reduce the effectiveness of clustered columnstore indexes if each partition has fewer than 1 million rows. Dedicated SQL pools automatically partition your data into 60 databases. So, if you create a table with 100 partitions, the result will be 6000 partitions.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql/best-practices-dedicated-sql-pool
You are creating dimensions for a data warehouse in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool.
You create a table by using the Transact-SQL statement shown in the following exhibit.
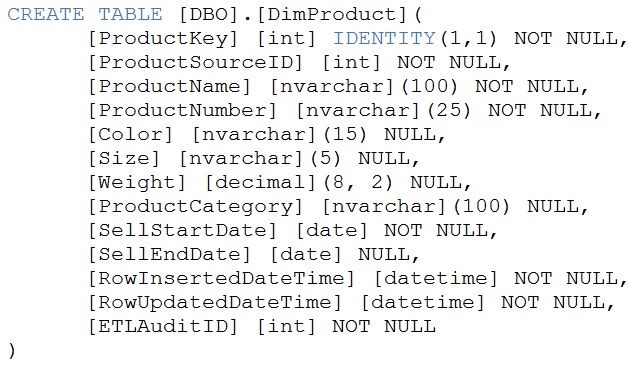
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
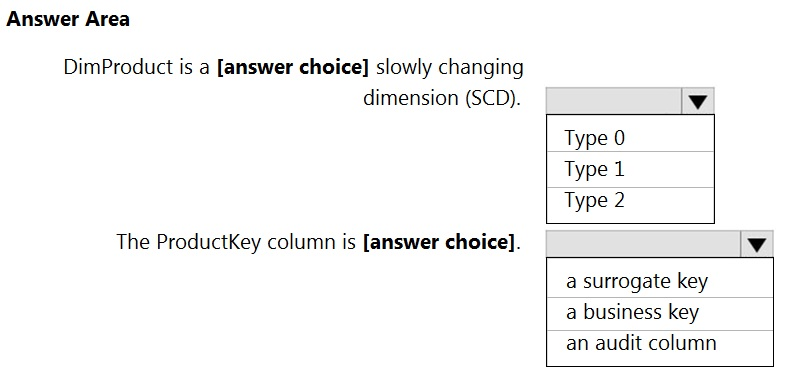
Box 1: Type 2
A Type 2 SCD supports versioning of dimension members. Often the source system doesn't store versions, so the data warehouse load process detects and manages changes in a dimension table. In this case, the dimension table must use a surrogate key to provide a unique reference to a version of the dimension member. It also includes columns that define the date range validity of the version (for example, StartDate and EndDate) and possibly a flag column (for example,
IsCurrent) to easily filter by current dimension members.
Incorrect Answers:
A Type 1 SCD always reflects the latest values, and when changes in source data are detected, the dimension table data is overwritten.
Box 2: Surrogate key
"In data warehousing, IDENTITY functionality is particularly important as it makes easier the creation of surrogate keys." Why ProductKey is certainly not a business key: "The IDENTITY value in Synapse is not guaranteed to be unique if the user explicitly inserts a duplicate value with 'SET IDENTITY_INSERT ON' or reseeds IDENTITY".
Type-1: Because here we are keeping, RowInsertedDate and RowUpdatedDate, and both are set to NOT NULL.
Surrogate Key: Because identity key is auto-incremented by System and not decided by business stakeholders.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/populate-slowly-changing-dimensions-azure-synapse-analytics-pipelines/3-choose-between-dimension-types
You are designing a fact table named FactPurchase in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool. The table contains purchases from suppliers for a retail store. FactPurchase will contain the following columns.
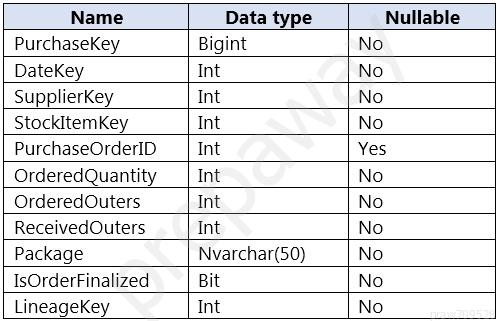
FactPurchase will have 1 million rows of data added daily and will contain three years of data.
Transact-SQL queries similar to the following query will be executed daily.
SELECT SupplierKey, StockItemKey, COUNT(*) FROM FactPurchase WHERE 1=1 AND DateKey >= 20210101 AND DateKey <= 20210131 GROUP By SupplierKey, StockItemKeyWhich table distribution will minimize query times?
replicated
hash-distributed on PurchaseKey
round-robin
hash-distributed on DateKey
Answer is hash-distributed on PurchaseKey
Hash-distributed tables improve query performance on large fact tables, and are the focus of this article. Round-robin tables are useful for improving loading speed.
Incorrect:
Not D: Do not use a date column. . All data for the same date lands in the same distribution. If several users are all filtering on the same date, then only 1 of the 60 distributions do all the processing work.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-tables-distribute
You are designing a data mart for the human resources (HR) department at your company. The data mart will contain employee information and employee transactions.
From a source system, you have a flat extract that has the following fields:
● EmployeeID
● FirstName
● LastName
● Recipient
● GrossAmount
● TransactionID
● GovernmentID
● NetAmountPaid
● TransactionDate
You need to design a star schema data model in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool for the data mart.
Which two tables should you create?
a dimension table for Transaction
a dimension table for EmployeeTransaction
a dimension table for Employee
a fact table for Employee
a fact table for Transaction
a dimension table for Employee: Dimension tables contain attribute data that might change but usually changes infrequently. For example, a customer's name and address are stored in a dimension table and updated only when the customer's profile changes. To minimize the size of a large fact table, the customer's name and address don't need to be in every row of a fact table. Instead, the fact table and the dimension table can share a customer ID. A query can join the two tables to associate a customer's profile and transactions.
a fact table for Transaction: Fact tables contain quantitative data that are commonly generated in a transactional system, and then loaded into the dedicated SQL pool. For example, a retail business generates sales transactions every day, and then loads the data into a dedicated SQL pool fact table for analysis.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-tables-overview