DP-203: Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
You have an Azure subscription that contains a logical Microsoft SQL server named Server1. Server1 hosts an Azure Synapse Analytics SQL dedicated pool named Pool1.
You need to recommend a Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) solution for Server1.
The solution must meet the following requirements:
- Track the usage of encryption keys.
- Maintain the access of client apps to Pool1 in the event of an Azure datacenter outage that affects the availability of the encryption keys.
What should you include in the recommendation?
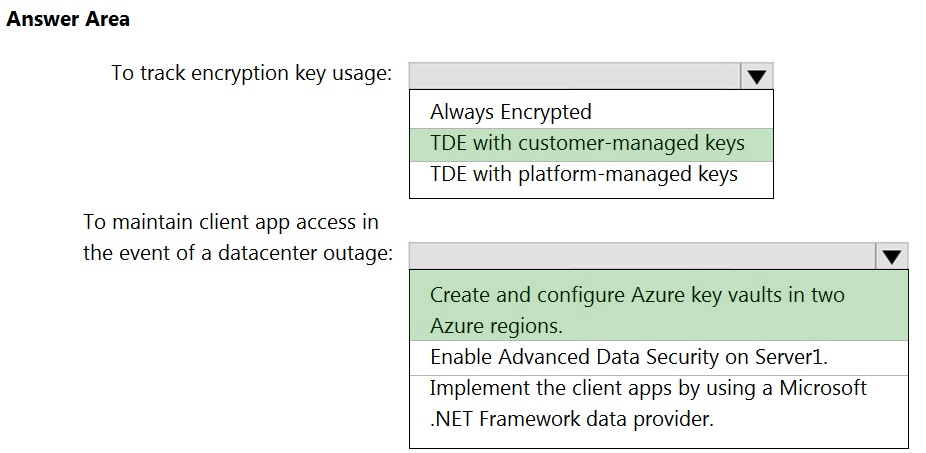
Box 1: TDE with customer-managed keys
Customer-managed keys are stored in the Azure Key Vault. You can monitor how and when your key vaults are accessed, and by whom. You can do this by enabling logging for Azure Key Vault, which saves information in an Azure storage account that you provide.
Box 2: Create and configure Azure key vaults in two Azure regions
The contents of your key vault are replicated within the region and to a secondary region at least 150 miles away, but within the same geography to maintain high durability of your keys and secrets.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/transparent-data-encryption-byok-overview
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/security/workspaces-encryption
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/key-vault/general/logging
You plan to create an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool.
You need to minimize the time it takes to identify queries that return confidential information as defined by the company's data privacy regulations and the users who executed the queues.
Which two components should you include in the solution?
sensitivity-classification labels applied to columns that contain confidential information
resource tags for databases that contain confidential information
audit logs sent to a Log Analytics workspace
dynamic data masking for columns that contain confidential information
Answers are;
sensitivity-classification labels applied to columns that contain confidential information
audit logs sent to a Log Analytics workspace
A: You can classify columns manually, as an alternative or in addition to the recommendation-based classification:
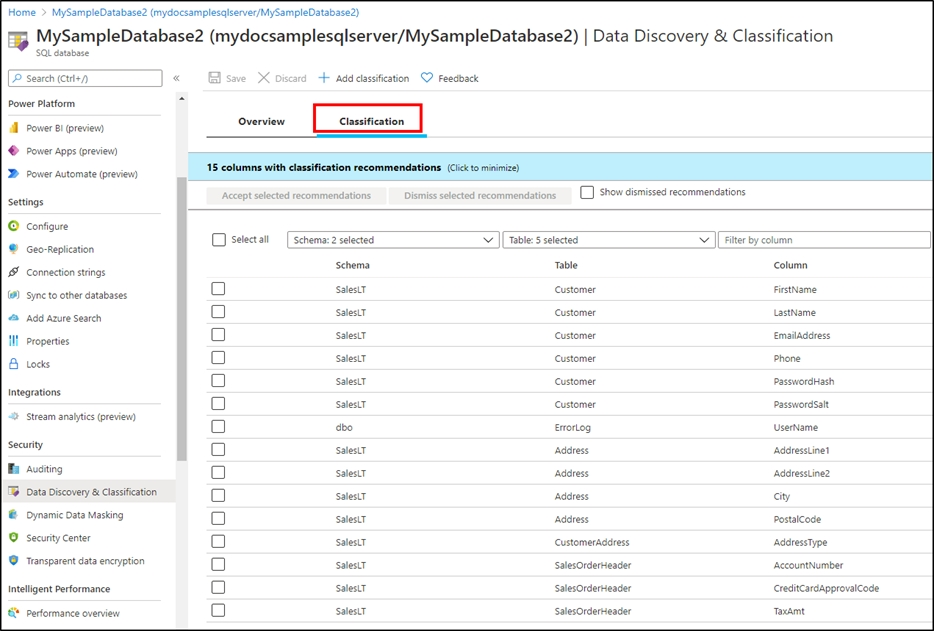
1. Select Add classification in the top menu of the pane.
2. In the context window that opens, select the schema, table, and column that you want to classify, and the information type and sensitivity label.
3. Select Add classification at the bottom of the context window.
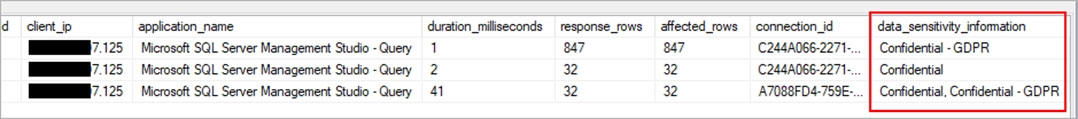
C: An important aspect of the information-protection paradigm is the ability to monitor access to sensitive data. Azure SQL Auditing has been enhanced to include a new field in the audit log called data_sensitivity_information. This field logs the sensitivity classifications (labels) of the data that was returned by a query. Here's an example:
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/data-discovery-and-classification-overview
You are designing an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics that will contain a table named Customers. Customers will contain credit card information.
You need to recommend a solution to provide salespeople with the ability to view all the entries in Customers. The solution must prevent all the salespeople from viewing or inferring the credit card information.
What should you include in the recommendation?
data masking
Always Encrypted
column-level security
row-level security
Answer is column-level security
"Column-level security simplifies the design and coding of security in your application, allowing you to restrict column access to protect sensitive data. "
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql-data-warehouse/column-level-security
You have a partitioned table in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool. You need to design queries to maximize the benefits of partition elimination. What should you include in the Transact-SQL queries?
JOIN
WHERE
DISTINCT
GROUP BY
Answer is WHERE
When you add the "WHERE" clause to your T-SQL query it allows the query optimizer accesses only the relevant partitions to satisfy the filter criteria of the query - which is what partition elimination is all about.
You implement an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics.
You have a large fact table that is 10 terabytes (TB) in size.
Incoming queries use the primary key SaleKey column to retrieve data as displayed in the following table:
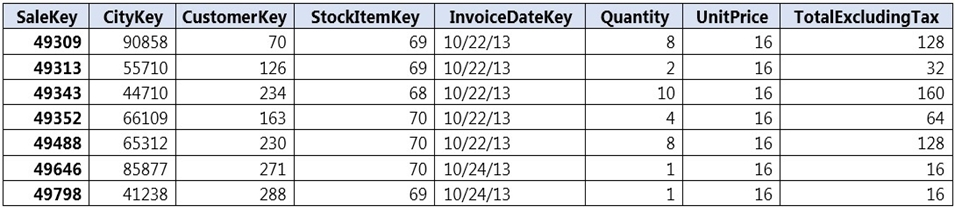
You need to distribute the large fact table across multiple nodes to optimize performance of the table.
Which technology should you use?
hash distributed table with clustered index
hash distributed table with clustered Columnstore index
round robin distributed table with clustered index
round robin distributed table with clustered Columnstore index
heap table with distribution replicate
Answer is hash distributed table with clustered Columnstore index
Hash-distributed tables improve query performance on large fact tables.
Columnstore indexes can achieve up to 100x better performance on analytics and data warehousing workloads and up to 10x better data compression than traditional rowstore indexes.
Incorrect Answers:
C, D: Round-robin tables are useful for improving loading speed.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-tables-distribute
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/indexes/columnstore-indexes-query-performance
You have an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool that contains a large fact table. The table contains 50 columns and 5 billion rows and is a heap.
Most queries against the table aggregate values from approximately 100 million rows and return only two columns.
You discover that the queries against the fact table are very slow.
Which type of index should you add to provide the fastest query times?
nonclustered columnstore
clustered columnstore
nonclustered
clustered
Answer is clustered columnstore
Clustered columnstore indexes are one of the most efficient ways you can store your data in dedicated SQL pool.
Columnstore tables won't benefit a query unless the table has more than 60 million rows.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql/best-practices-dedicated-sql-pool
You have an enterprise data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics.
Using PolyBase, you create an external table named [Ext].[Items] to query Parquet files stored in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 without importing the data to the data warehouse.
The external table has three columns.
You discover that the Parquet files have a fourth column named ItemID.
Which command should you run to add the ItemID column to the external table?
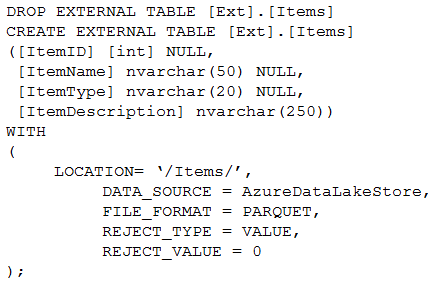



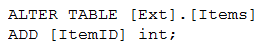
ALTER statement is not supported on external table, you need to DROP it and CREATE it again
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-explorer/kusto/management/external-sql-tables
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/create-external-table-transact-sql
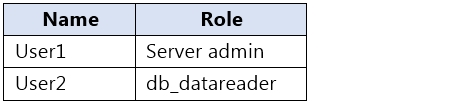
You have an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool that contains the users shown in the following table.
User1 executes a query on the database, and the query returns the results shown in the following exhibit.
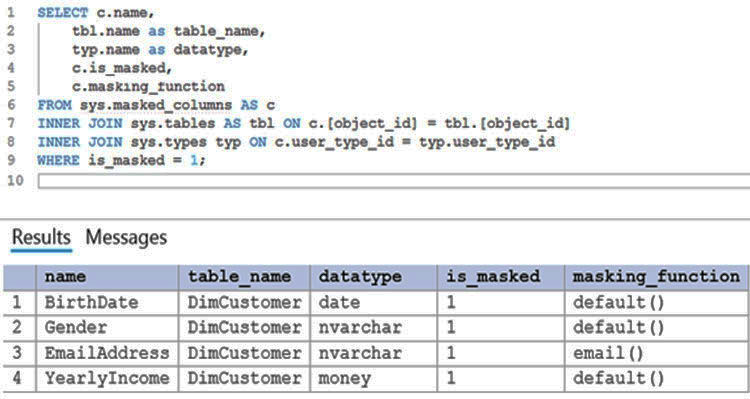
User1 is the only user who has access to the unmasked data.
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.

Box 1: 0
The YearlyIncome column is of the money data type.
The Default masking function: Full masking according to the data types of the designated fields
Use a zero value for numeric data types (bigint, bit, decimal, int, money, numeric, smallint, smallmoney, tinyint, float, real).
Box 2: the values stored in the database
Users with administrator privileges are always excluded from masking, and see the original data without any mask.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/dynamic-data-masking-overview
You have a table in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool. The table was created by using the following Transact-SQL statement.

You need to alter the table to meet the following requirements:
● Ensure that users can identify the current manager of employees.
● Support creating an employee reporting hierarchy for your entire company.
● Provide fast lookup of the managers' attributes such as name and job title.
Which column should you add to the table?
[ManagerEmployeeID] [smallint] NULL
[ManagerEmployeeKey] [smallint] NULL
[ManagerEmployeeKey] [int] NULL
[ManagerName] [varchar](200) NULL
Answer is [ManagerEmployeeKey] [int] NULL
We need an extra column to identify the Manager. Use the data type as the EmployeeKey column, an int column.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/analysis-services/tabular-models/hierarchies-ssas-tabular
You have a SQL pool in Azure Synapse.
You plan to load data from Azure Blob storage to a staging table. Approximately 1 million rows of data will be loaded daily. The table will be truncated before each daily load.
You need to create the staging table. The solution must minimize how long it takes to load the data to the staging table.
How should you configure the table?
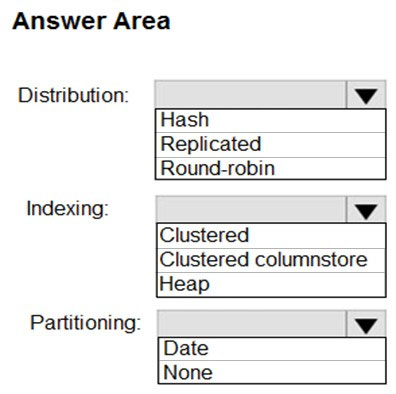
Answer is Round-Robin Heap None
Round-robin - this is the simplest distribution model, not great for querying but fast to process
Heap - The term heap basically refers to a table without a clustered index. Adding a clustered index to a temp table makes absolutely no sense and is a waste of compute resources for a table that would be entirely truncated daily. no clustered index = heap.
No partitions - Partitioning by date is useful when stage destination has data because you can hide the inserting data’s new partition (to keep users from hitting it), complete the load and then unhide the new partition.
However, in this question it states, “the table will be truncated before each daily load”, so, it appears it’s a true Staging table and there are no users with access, no existing data, and I see no reason to have a Date partition.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql/data-loading-best-practices
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql/develop-tables-overview